Circular Motion hidden concepts
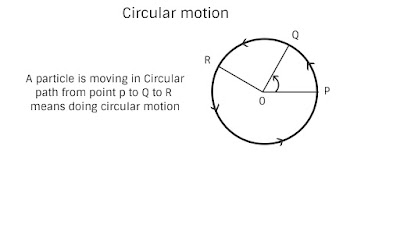
Circular motion hidden concept in this topic we will learn the concept for circular motion which we have not learned before as from the name we know that circular motion means related to circle motion but not only this more than circle motion is circular motion all concept for different parameter use in this motion we cover in depth concept its definition and derivation in first post we have learn the basic concept for circular motion you can refer post Basic concept circular motion here we will see depth concept of circular motion this motion is 2-D motion because both x and y coordinate position changes from reference point when a particle or body do circular motion see the picture below.
Angular displacement is 𝛳 this is measure in two unit one is called degree and other is radian (S.I unit) as we know that degree to radian is converted like one complete rotation means 360 degree.
360⁰ = 2𝛑 rad 45⁰ = 𝛑/4 rad
180⁰ = 𝛑 rad 60⁰ = 𝛑/3 rad
90⁰ = 𝛑/2 rad 30⁰ = 𝛑/6 rad
above is radian to degree converter so SI unit is radian
Angular displacement 𝛳 is a vector quantity and it is a axial vector means along axis its direction will be away from the plan use right hand thumb rule put your finger in motion direction and curl your finger thumb pointing will give the direction angular displacement dimension is M⁰ L⁰ T⁰ it is dimensionless quantity it has unit radian but no dimension rear quantity now relation with angular displacement and linear displacement we know
2𝛑 (Angular displacement) = 2𝛑r (linear displacement )
𝛳(angular displacement ) = r𝛳 (linear displacement )
let s = linear displacement then s = r𝛳 (this can't be written in vector form because 𝛳 and s direction are not same now come to angular velocity as we know linear velocity is v = ∆s/∆t hence angular velocity will be 𝛚(omega) =∆𝛳/∆t angular velocity 𝛚 is a vector quantity having direction same as angular displacement its SI unit is rad/s dimension M⁰L⁰/T .
Vavg = ∆s/∆t for long time period for small time Vins = ds/dt similarly 𝛚avg = ∆𝛳/∆t for long time period, for small time
𝛚ins = d𝛚/dt .
take an example 𝛳 = 2t² +2 then find 𝛚 in 2 s and at 2s
𝛚avg in 0 to 2 sec put t=0 then 𝛳 = 2, put t=2s then 𝛳= 2*2*2+2 = 10
hence 𝛚avg = ∆𝛳/∆t = (10-2)/2 =8/2 = 4rad/s
now at 2s means 𝛚ins = d𝛳/dt = 2*2t+0 = 4t now put t=2
𝛚ins = 4*2 = 8rad/s.
Now relation between linear velocity and angular velocity
we know that linear velocity V = ∆s/∆t and 𝛚 = ∆𝛳/∆t and we have seen s = r𝛳 or 𝛳 = s/r put in above equation 𝛚 = ∆𝛳/∆t = ∆s/r/∆t
here r is radius and constant 𝛚 = 1/r*(∆s/∆t) = v/r hence v = 𝛚r
𝛚 = v/r concept which below equation is correct
→ →
v = 𝛚r or v = 𝛚r here vector equation is wrong because direction of v and direction of 𝛚 is not same 𝛚 direction is along the axis and v direction is always changing in circular path tangent to radius so scalar equation is correct.
now v = 𝛚r is only correct for circle not for all angular velocity cases in circle one condition is very unique angle between v and radius is always 90⁰ means it is clear that the equation v = 𝛚r velocity must perpendicular to radius to use this formula very important point or 𝛚 = v/r = velocity perpendicular/r
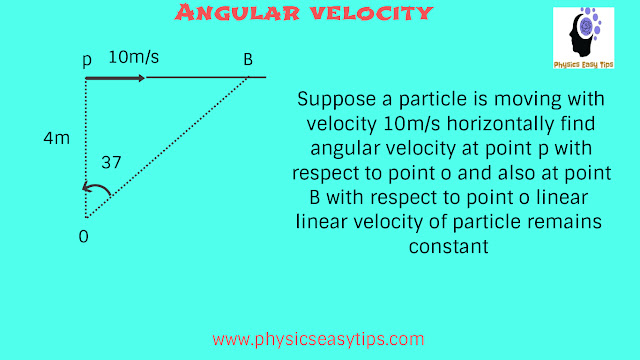
see below question to understand the concepts.
𝛚 = v(perpendicular)/r = 10/4 = 2.5 rad/s but when particle will be at point B then radius will be OB and we have to take v(perpendicular component ) to OB now we need calculate OB and perpendicular component of velocity to find angular velocity now from triangle OB = 5 now take perpendicular velocity component to OB it will be 10cos37 hence 𝛚 angular velocity at B = 10cos37/OB = 10*4/5*1/5 = 8/5 = 1.6rad/s hence it is clear that for angular velocity perpendicular component of velocity is taken for using formula 𝛚 = v/r and other important point linear velocity is constant but angular velocity is changing is decreasing means angular velocity is not related to circle it is a general term use anywhere see the below question for angular velocity.
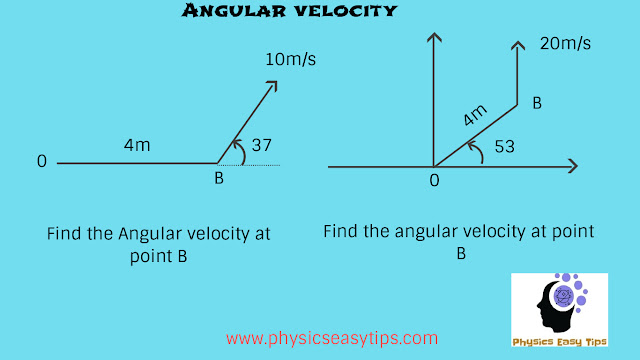
here from first question angular velocity at point B with respect to 0 𝛚 will be 𝛚 = velocity perpendicular/OB = 10sin37/OB
𝛚 = 10sin37/4 = 10*3/5*1/4 = 6/4 = 1.5rad/s.
for second question take perpendicular linear velocity component to OB it will be angular velocity 𝛚 with respect to 0
𝛚 = 20sin37/4 = 20*3/5*1/4 = 3rad/s
now if 0 and B both point are moving then you have to take relative perpendicular velocity component and divide distance this is angular velocity concept hence you write in circular motion
𝛚 = v/r
→ → →
v = 𝛚 × r this equation is correct
because radius is always perpendicular to velocity i hope now your concept for angular velocity is clear
Frequency : this is define as number of revolution in one sec it is denoted by f in one complete revolution angular displacement =2𝛑 hence in one sec 𝛳 = 2𝛑 f now 𝛚 = ∆𝛳/∆t = 2𝛑 f/1sec = 2𝛑 f
𝛚 = 2𝛑 f this is relation between angular velocity with frequency.
Time period : this is define as time taken to complete on revolution
if frequency is f then time period will be 1/f hence T = 1/f hence we can write 𝛚 = 2𝛑 f = 2𝛑/T now we will continue in next post i hope you have enjoyed learning Circular Motion hidden concepts
thanks for reading.
dated 9th Sep 2018
here from first question angular velocity at point B with respect to 0 𝛚 will be 𝛚 = velocity perpendicular/OB = 10sin37/OB
𝛚 = 10sin37/4 = 10*3/5*1/4 = 6/4 = 1.5rad/s.
for second question take perpendicular linear velocity component to OB it will be angular velocity 𝛚 with respect to 0
𝛚 = 20sin37/4 = 20*3/5*1/4 = 3rad/s
now if 0 and B both point are moving then you have to take relative perpendicular velocity component and divide distance this is angular velocity concept hence you write in circular motion
𝛚 = v/r
→ → →
v = 𝛚 × r this equation is correct
because radius is always perpendicular to velocity i hope now your concept for angular velocity is clear
Frequency : this is define as number of revolution in one sec it is denoted by f in one complete revolution angular displacement =2𝛑 hence in one sec 𝛳 = 2𝛑 f now 𝛚 = ∆𝛳/∆t = 2𝛑 f/1sec = 2𝛑 f
𝛚 = 2𝛑 f this is relation between angular velocity with frequency.
Time period : this is define as time taken to complete on revolution
if frequency is f then time period will be 1/f hence T = 1/f hence we can write 𝛚 = 2𝛑 f = 2𝛑/T now we will continue in next post i hope you have enjoyed learning Circular Motion hidden concepts
thanks for reading.
dated 9th Sep 2018

No comments:
Post a Comment